News
-
Alterations in the gut microbiota have gained increasing recognition as a key contributor to the development and progression of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In particular, dysbiosis—a disruption in the normal balance and diversity of gut microbial communities—has been linked to a range of metabolic disturbances, including systemic inflammation, impaired glucose metabolism, and…
-
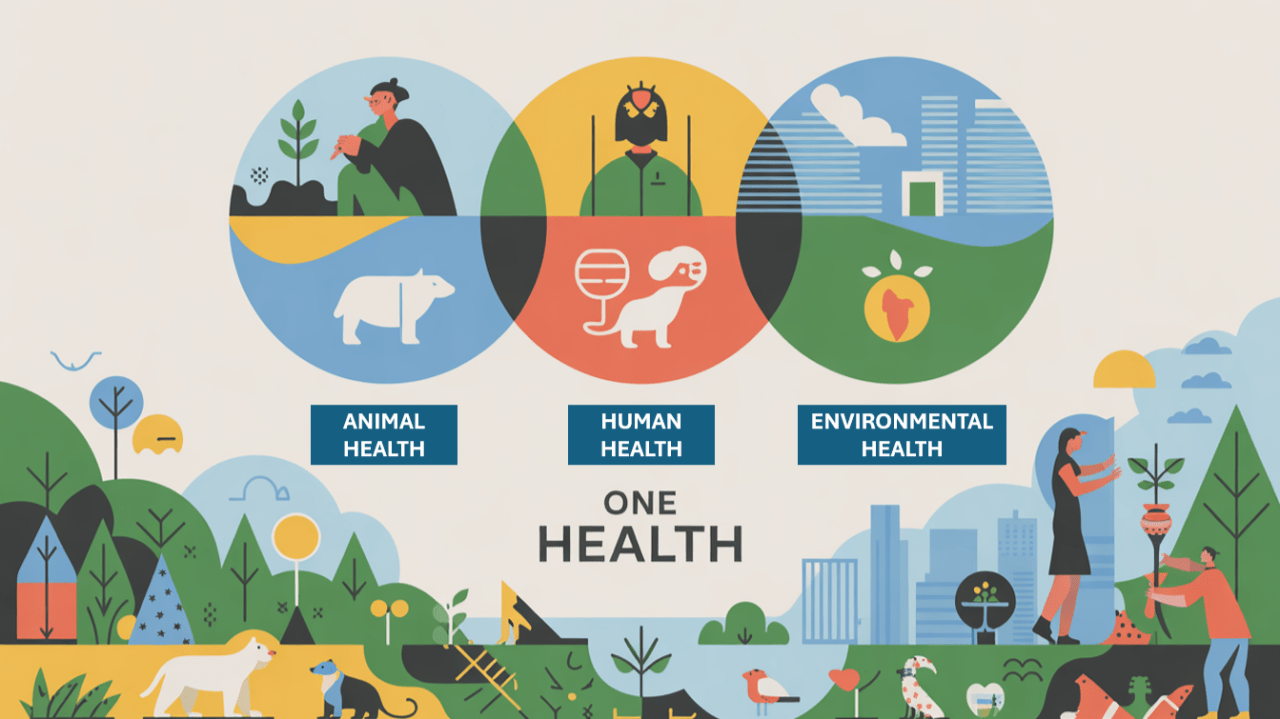
The One Health concept emphasizes the interdependence of human, animal, and environmental health. It has evolved into a multidisciplinary framework addressing complex health challenges such as zoonotic diseases, antimicrobial resistance, and food safety, through interdisciplinary collaboration and systems thinking. Foundations and scope One Health emerged from the recognition that human health cannot be isolated from…
-
In the rapidly evolving landscape of biomedical innovation, the intersection of biotechnology and microfluidics has catalyzed the emergence of Organ-on-a-Chip (OoC) technology—microengineered systems that mimic the physiological and functional characteristics of human organs. This cutting-edge approach is transforming how we study disease mechanisms, evaluate drugs, and tailor therapeutic strategies in personalized medicine. What Are Organ-on-a-Chip…
-

Diet is one of the most influential and immediate factors shaping the composition and function of the gut microbiota. Nutritional intake can rapidly alter microbial diversity, metabolic activity, and overall ecosystem balance—impacting health outcomes, disease susceptibility, and nutrient processing. Understanding these dynamics is essential for advancing personalized nutrition and microbiome-based interventions. Curious about how your…
-

The concept that our gut and brain are deeply connected is no longer speculative—it’s now a cornerstone of biomedical research. The gut–brain axis, a bidirectional communication network linking the gastrointestinal tract with the central nervous system, is increasingly understood to be regulated by the trillions of microbes residing in our gut microbiota (Cryan & Dinan,…
-

Diet plays a fundamental role in shaping the composition and functionality of the canine gut microbiota, surpassing environmental factors in its influence. Recent advances in next-generation sequencing have enabled detailed analysis of fecal samples, allowing researchers to uncover complex interactions between the host and its microbiota. The balance of macronutrients—particularly proteins, carbohydrates, and fibers—has a…
-

Microbiome-driven adaptations are fundamental to how both domesticated and wild animals respond to environmental challenges. The gut microbiota plays a central role in regulating nutrition, immune function, and resilience to environmental stressors. Notably, significant differences in microbiome composition and functionality are observed between wild and domesticated species, largely influenced by diet, habitat, and human interaction.…
-

Similar to humans, the gut microbiota of dogs is a diverse and dynamic community of microorganisms that plays a vital role in maintaining health. It contributes significantly to metabolism, immune function, and resistance to disease. In recent years, research has increasingly focused on understanding the composition and development of the canine gut microbiota, the factors…
-
Gut check before takeoff! Travel—even a quick getaway—can stir up dramatic changes in your gut microbiota. Whether you’re hopping continents or road-tripping for a weekend, exposure to new environments, foods, and microbes can disrupt your internal balance, triggering digestive symptoms like diarrhoea—or sneakily shifting your gut without you noticing a thing. These fluctuations, driven by…
-

Every year on 18 June, Sustainable Gastronomy Day invites the global community to reflect on the intertwined destinies of cuisine, culture, and ecological integrity. At the heart of this celebration lies a question that extends far beyond the plate: How do our food choices reverberate through the invisible ecosystems of the human gut? Sustainable dietary patterns…
